Post Syndicated from Bobby Whyte original https://www.raspberrypi.org/blog/teaching-programming-in-primary-school-tippsee/
Every young learner needs a successful start to their learning journey in the primary computing classroom. One aspect of this for teachers is to introduce programming to their learners in a structured way. As computing education is introduced in more schools, the need for research-informed strategies and approaches to support beginner programmers is growing. Over recent years, researchers have proposed various strategies to guide teachers and students, such as the block model, PRIMM, and, in the case of this month’s seminar, TIPP&SEE.

We are committed to make computing and creating with digital technologies accessible to all young people, including through our work with educators and researchers. In our current online research seminar series, we focus on computing education for primary-aged children (K–5, ages 5 to 11). In the series’ second seminar, we were delighted to welcome Dr Jean Salac, researcher in the Code & Cognition Lab at the University of Washington.

Jean’s work sits across computing education and human-computer interaction, with an emphasis on justice-focused computing for youth. She talked to the seminar attendees about her work on developing strategies to support primary school students learning to program in Scratch. Specifically, Jean described an approach called TIPP&SEE and how teachers can use it to guide their learners through programming activities.
What is TIPP&SEE?
TIPP&SEE is a metacognitive approach for programming in Scratch. The purpose of metacognitive strategies is to help students become more aware of their own learning processes.

TIPP&SEE scaffolds students as they learn from example Scratch projects: TIPP (Title, Instructions, Purpose, Play) is a scaffold to read and run a Scratch project, while SEE (Sprites, Events, Explore) is a scaffold to examine projects more deeply and begin to adapt them.
Using, modifying and creating
TIPP&SEE is inspired by the work of Irene Lee and colleagues who proposed a progressive three-stage approach called Use-Modify-Create. Following that approach, learners move from reading pre-existing programs (“not mine”) to adapting and creating their own programs (“mine”) and gradually increase ownership of their learning.
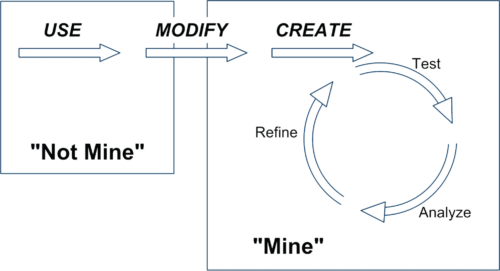
Proponents of scaffolded approaches like Use-Modify-Create argue that engaging learners in cycles of using existing programs (e.g. worked examples) before they move to adapting and creating new programs encourages ownership and agency in learning. TIPP&SEE builds on this model by providing additional scaffolding measures to support learners.
Impact of TIPP&SEE
Jean presented some promising results from her research on the use of TIPP&SEE in classrooms. In one study, fourth-grade learners (age 9 to 10) were randomly assigned to one of two groups: (i) Use-Modify-Create only (the control group) or (ii) Use-Modify-Create with TIPP&SEE. Jean found that, compared to learners in the control group, learners in the TIPP&SEE group:
- Were more thorough, and completed more tasks
- Wrote longer scripts during open-ended tasks
- Used more learned blocks during open-ended tasks
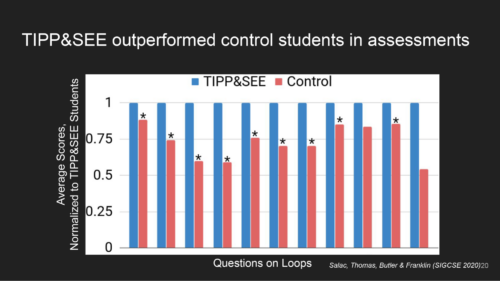
In another study, Jean compared how learners in the TIPP&SEE and control groups performed on several cognitive tests. She found that, in the TIPP&SEE group, students with learning difficulties performed as well as students without learning difficulties. In other words, in the TIPP&SEE group the performance gap was much narrower than in the control group. In our seminar, Jean argued that this indicates the TIPP&SEE scaffolding provides much-needed support to diverse groups of students.
Using TIPP&SEE in the classroom
TIPP&SEE is a multi-step strategy where learners start by looking at the surface elements of a program, and then move on to examining the underlying code. In the TIPP phase, learners first read the title and instructions of a Scratch project, identify its purpose, and then play the project to see what it does.

In the second phase, SEE, learners look inside the Scratch project to click on sprites and predict what each script is doing. They then make changes to the Scratch code and see how the project’s output changes. By changing parameters, learners can observe which part of the output changes as a result and then reason how each block functions. This practice is called deliberate tinkering because it encourages learners to observe changes while executing programs multiple times with different parameters.

You can read more of Jean’s research on TIPP&SEE on her website. There’s also a video on how TIPP&SEE can be used, and free lesson resources based on TIPP&SEE are available in Elementary Computing for ALL and Scratch Encore.
Learning about learning in computing education
Jean’s talk highlighted the need for computing to be inclusive and to give equitable access to all learners. The field of computing education is still in its infancy, though our understanding of how young people learn about computing is growing. We ourselves work to deepen our understanding of how young people learn through computing and digital making experiences.
In our own research, we have been investigating similar teaching approaches for programming, including the use of the PRIMM approach in the UK, so we were very interested to learn about different approaches and country contexts. We are grateful to Dr Jean Salac for sharing her work with researchers and teachers alike. Watch the recording of Jean’s seminar to hear more:
Free support for teaching programming and more to primary school learners
If you are looking for more free resources to help you structure your computing lessons:
- Download our comprehensive classroom resources in The Computing Curriculum, which includes units of programming lessons for age 5 and upwards.
- Take one of our online courses about teaching computing. The course Teaching programming to 5- to 11-year-olds is especially relevant to this seminar.
- Read The Big Book of Computing Pedagogy, a special edition of our Hello World magazine.
Join our next seminar
In the next seminar of our online series on primary computing, I will be presenting my research on integrated computing and literacy activities. Sign up now to join us for this session on Tues 7 March:
As always, the seminars will take place online on the first Tuesday of the month at 17:00–18:30 UK time. Hope to see you there!
The post Supporting beginner programmers in primary school using TIPP&SEE appeared first on Raspberry Pi.









