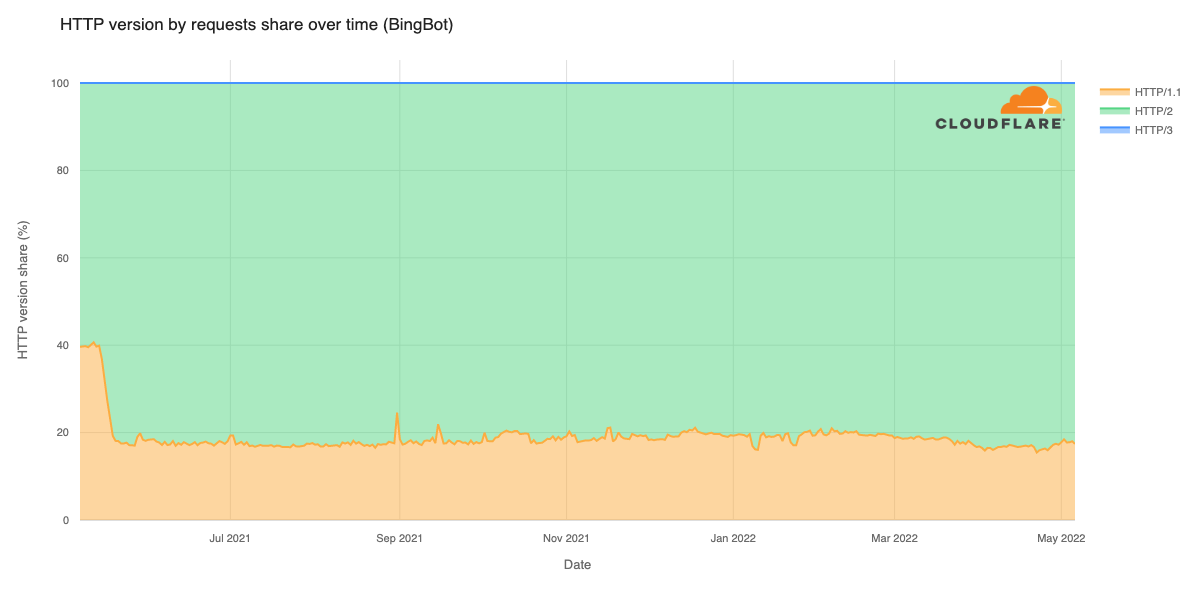
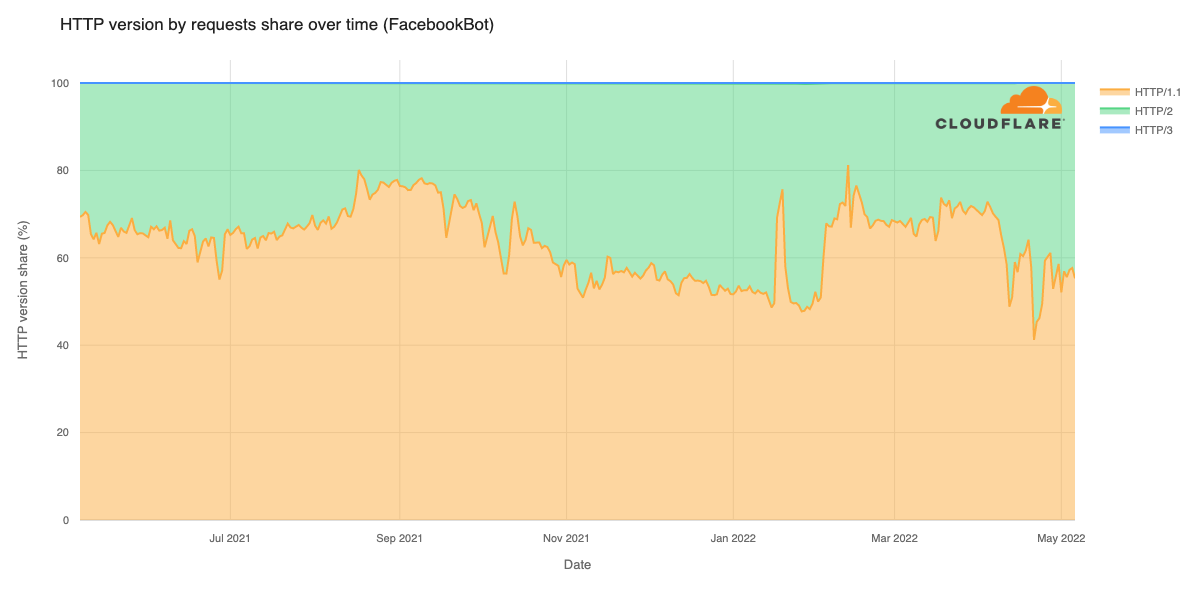
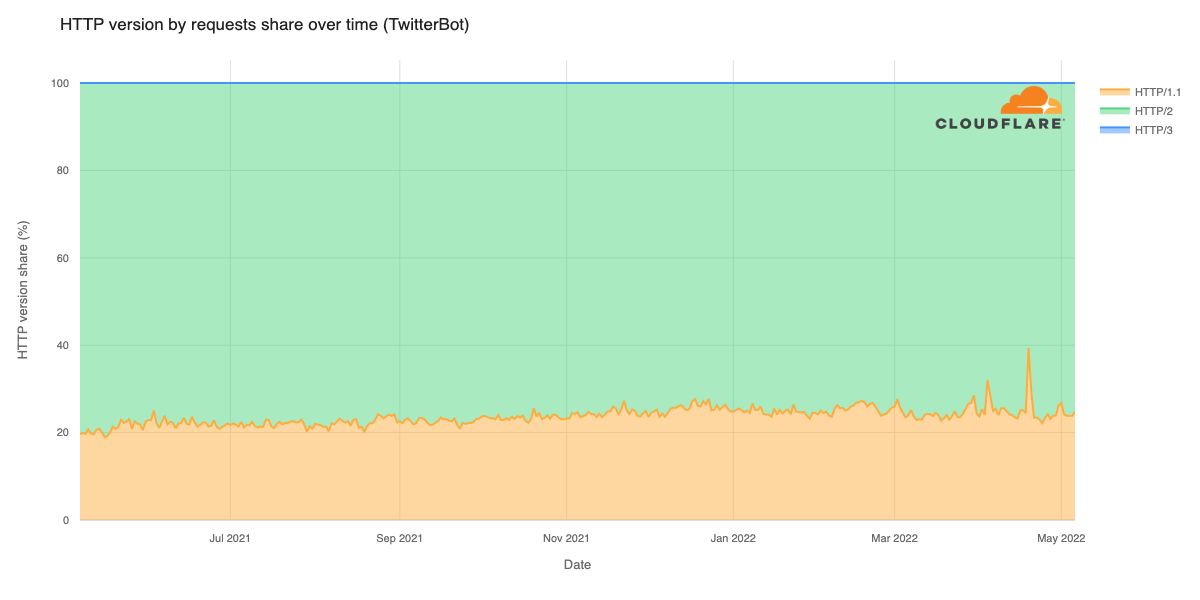
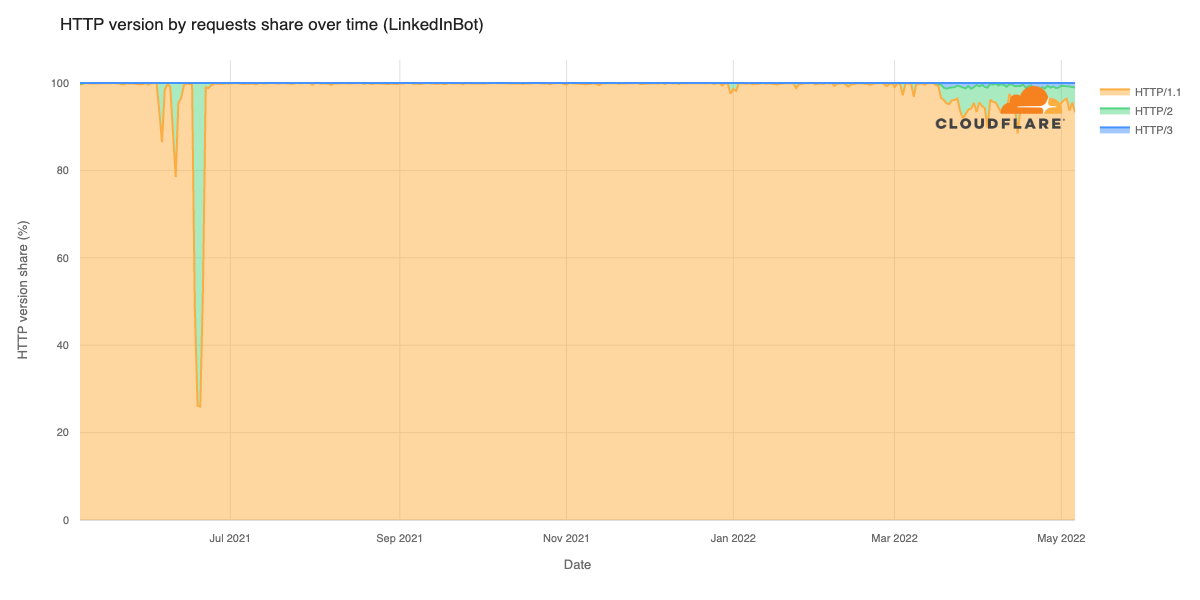
Post Syndicated from Мирослав Зафиров original https://toest.bg/nadim-shehadi-interview/
Надим Шехади (р. 1956) е изпълнителен директор на Академичния център на Ливано-американския университет в Ню Йорк и асоцииран сътрудник в Кралския институт за международни отношения („Чатъм Хаус“), където по-рано е ръководил програмата за Близкия изток. Бил е директор на Центъра за източносредиземноморски изследвания „Фарес“ към Факултета по право и дипломация в Университета „Тъфтс“ и дългогодишен директор на „Ливански изследвания“ в колежа „Св. Антоний“ към Оксфордския университет. Той е водещ учен по въпросите на Близкия изток и Северна Африка и е консултант на няколко правителства и международни организации, в т.ч. и на Европейския съюз. Негови статии са публикувани в големи международни новинарски издания, като „Ню Йорк Таймс“, „Гардиън“ и Си Ен Ен.
По повод наскоро състоялите се парламентарни избори в Ливан, а и цялостната обстановка в Близкия изток в светлината на настоящите глобални кризи, с г-н Шехади разговаря Мирослав Зафиров.
Според мнозина Ливан е своеобразен паноптикум на Близкия изток. Доколкото това е вярно, смятате ли, че е трудно да се предвиди какво е бъдещето на Близкия изток? Вече много години регионът сякаш не може да намери себе си.
Мнозинството от дисидентите, интелектуалците и хората на бизнеса намираха пристан в Бейрут, където свободно можеха да упражняват своите професии и да изразяват себе си. На практика Бейрут беше поле на сблъсък на идеи, които едва по-късно намираха аудитория на други места. Ливанската гражданска война от 1975 до 1990 г. се превърна в лаборатория на съперничещите си идеологии на исляма и национализма, на светското и религиозното начало, на шиитския и сунитския ислям, на либерализма и авторитаризма, и т.н.
Ние вече не се намираме в това положение, днес ще откриете този дебат по-скоро в Лондон, отколкото в Бейрут. Регионът постепенно навлезе в спиралата на непредсказуемостта – процес, започнал още през 50-те години на XX век. Възходът на светските националистически военни режими, който постепенно изтласка традиционната аристокрация и елитите, останали от Османската империя, показа истинското си лице – това на репресивния режим. Този режим бе особено безпощаден спрямо движенията, принадлежащи към политическия ислям. Но не само ислямистите бяха целта, скоро жертви на преследвания станаха левите политически течения и либералите.
Вероятно всичко това е в дъното на т.нар. Арабска пролет и е в основата на исканията на младото поколение за решително противопоставяне срещу доминацията на организации като милициите, свързани с иранския Корпус на стражите на Ислямската революция. Борбата беше срещу опита на КСИР да получи надмощие на всички места, където институционалността на държавата отслабваше или отсъстваше.
Какво е мнението Ви за наскоро проведените парламентарни избори в Ливан? След години на нарастващо напрежение, икономическа криза и политическа нестабилност смятате ли, че страната е готова да излекува своите рани?
Изборите в Ливан наподобяват тези в Ирак от 2021 г., доколкото резултатите демонстрираха намаляване на влиянието на проиранските партии и милиции. И в двете държави имаше сходно по дух обществено настроение. В случая с Ливан „Хизбулла“ се ползваше с абсолютния контрол над шиитските гласове, а коалицията ѝ с другата шиитска партия – „Амал“, ѝ осигури 27 места в парламента, въпреки че партиите загубиха двете места, които не бяха предвидени за шиитите.
Системата в Ливан дава възможност на „Хизбулла“ и нейните съюзници да упражняват правото на вето върху всички назначения: председател на парламента, министър-председател, президент и т.н. Коалицията е в състояние да парализира всеки изборен процес, докато условията, налагани от „Хизбулла“, не бъдат изпълнени. Те направиха това през 2006 г., когато окупираха центъра на Бейрут и парализираха страната за 19 месеца. Кризата приключи едва със Споразумението от Доха от 2008 г., в което ветото на „Хизбулла“ беше на практика институционализирано. По-късно отново шиитската коалиция блокира политическия процес за нови 29 месеца – между 2013 и 2016 г., когато Ливан съществуваше без президент, изборите за парламент бяха забавени, а правителството беше лишено от възможност да функционира. И всичко това – за да може отново „Хизбулла“ да наложи избора си за държавен глава.
На 15 май 2022 г. бяха проведени парламентарни избори в Ливан, на които за първи път след десетилетия на доминация „Хизбулла“ загуби мнозинството си. Коалицията, водена от шиитското движение, разполага с 62 от 128 места в Народното събрание. Противниците на шиитската коалиция – в т.ч. и финансираната от Саудитска Арабия християнска партия „Ливански сили“ – спечелиха мнозинство. Сред големите изненади бе и победата на движението на друзкия лидер Уалид Джумблат над неговия исторически противник и лидер на другата основна друзка фамилия – Талал Арслан. Джумблат е известен с позицията си срещу влиянието на Сирия в Ливан. Заслужава внимание и ниската избирателна активност сред сунитското население, като много от поддръжниците на бившия премиер Саад Харири по този начин изразиха подкрепа за сина на загиналия през 2005 г. Рафик Харири и решението му да не участва в изборите.
Какъв е Вашият анализ на парламентарните резултати? Наистина ли говорим за постепенно отслабване на „Хизбулла“?
Резултатите демонстрираха нарастваща опозиция срещу „Хизбулла“, но тези резултати засегнаха единствено нейните нешиитски съюзници. Основно „пострадаха“ просирийските кандидат-депутати, чиито имена бяха включени в списъците под натиска на Сирия или на „Хизбулла“. Всичко това обаче няма да повлияе особено на позициите на партията, защото хегемонията ѝ над шиитите остава, както и влиянието ѝ над шиитските депутати. Тя е в състояние да диктува своите условия.
Важно е да се отбележи, че общите листи между „Амал“ и „Хизбулла“ са резултат от споразумение, постигнато след тригодишни преговори. Лидерът на „Амал“ Набих Бери беше заявил, че „Хизбулла“ олицетворява Дракула, защото живее за сметка на кръвта, която пролива, и обвини партията, че е отговорна за убийството на повече шиити, отколкото самият Израел. Няколко от водещите фигури в „Амал“ бяха убити, а други напуснаха страната или бяха изолирани, докато най-сетне не беше сключено споразумението за обща листа. По този начин това, което по-късно стана известно като „шиитското дуо“, видя бял свят и не позволи появата на нови независими политически гласове сред шиитите. В шиитските части на Ливан общата листа получи почти пълна подкрепа. Подобно на вота в един авторитарен режим, 97,6 % от гласовете на шиитите бяха за коалицията между „Амал“ и „Хизбулла“.
През 2020 г. в статия за „Ню Йорк Таймс“ Лина Мунзер написа, че въпреки убеждението си, че могат да преживеят всичко, ливанците се оказаха излъгани. Вие съгласен ли сте с нея? И ако е така, кое е онова нещо, което ливанците не успяха да преживеят – последиците от Споразумението от Таиф? Възхода на „Хизбулла“ през годините? Сирийската война, а преди нея – израелската окупация в Южен Ливан?
Признавам си, че не си спомням тази статия, но дори последните две години в Ливан бяха достатъчно трудни. Мнозина ливанци осъзнаха, че повече не са в състояние да „преживеят всичко“. Ливанците трябваше да избират между няколко дилеми – конфронтация или компромис, сигурност или свобода, война или мир, и т.н. Но в крайна сметка политическата ни система не можа да издържи на постоянния натиск на „Хизбулла“. Това е все едно да играете футбол под прицела на снайперист, по чиято воля във всеки момент всеки от играчите може да бъде елиминиран. Някои ливанци обвиняват системата, но аз лично смятам, че никоя система не е в състояние да понесе подобен партньор и да оцелее под подобен натиск.
Вие сте известен с позицията си спрямо Иран. Предвид санкциите смятате ли, че Иран някак успя да оцелее въпреки всички атаки срещу себе си? Също така успя ли Техеран да намери изход от кризата в Сирия?
Моето отношение не е спрямо Иран, а спрямо регионалната криминална структура, от която страдат включително и иранските граждани – по същия начин, по който жертви са и сирийците, и иракчаните, а донякъде – и палестинците и йеменците. Регионът е заложник на КСИР и неговите военни съюзници. Всички те използват един и същи набор от средства: убийства, парализа на политическата система, натиск.
Ние всички живеем в условията на последиците от войната между Иран и Ирак от 1980 г. Войната позволи на режима на Саддам Хюсеин да консолидира властта си и да наложи пълен контрол над Ирак, така както стори и КСИР в Иран. „Хизбулла“ е продължение на този процес, използвайки същата методология. Днес обаче ние виждаме ново поколение от хора, които се изправят срещу описаната тенденция в Ливан, Ирак, а и в самия Иран.
През 2011 и 2012 г., благодарение на Вашата помощ, София успя да стане домакин на първата истинска среща на сирийската опозиция. Мнозина бяха скептични, но срещата произведе първата обща декларация, която, за съжаление, впоследствие беше неглижирана от някои страни. Днес, десет години по-късно, какъв е изходът от продължаващата криза в Сирия, или тя вече е хроничен проблем, подобно на палестинския въпрос – две кризи, които влияят на стабилността в региона?
От работата си по Сирия мога да направя два извода. Първият сочи, че беше грешка да се опитваме да формираме опозиция на режима в Дамаск. Подобен опит всъщност беше в полза на самия режим, тъй като това доведе до необходимостта самата опозиция да доказва своята легитимност и жизнеспособност. Дамаск се възползва от ситуацията, тъй като цялото световно обществено внимание се съсредоточи върху опозицията, а не върху деянията на режима.
Появата на опозицията също така позволи на медиите да започнат да говорят за водена в Сирия „гражданска война“, като по този начин се измести акцентът от темата за революцията, която настъпи там, и престъпленията, които режимът на Башар ал Асад извършваше срещу своите граждани, за да остане на власт. Опозицията беше под натиск да докаже легитимността си, че е обединена, че е светска, че има силно ръководство и т.н. Докато всъщност някаква форма на плурализъм, а и отсъствие на единно ръководство можеше да се смята за положителен феномен в нововъзникващото демократично общество след периода „Асад“.
Вторият извод, който мога да направя, говори за това, че в резултат на над 50-годишното управление на режима на семейство Асад сирийското общество беше доведено до ниво на политическа нефункционалност. Хората се надигнаха, излизайки анонимно по улиците, но едва сблъскали се с форма на лидерство или алтернативни групи, у тях веднага се появи едно вродено недоверие и подозрителност. Подозрение, което режимът и неговите служби за сигурност съзнателно подклаждаха.
Попаднеш ли в затвора, от теб ще бъде поискано да станеш доносник. Тези, които откажат, никога не напускат затвора и загиват там. Прекаралите години в затвора и хората, чиито семейства са страдали, веднага попадат под подозрение единствено заради това, че са успели да оцелеят. Всичко това наподобява поведението на ЩАЗИ и останалите служби за сигурност. По тази причина беше безсмислено да се опитваме да формираме опозиция, при условие че режимът бе все на мястото си, очаквайки, че ще можем да го заменим. Имаше един мъничък Башар във всеки човек в Сирия по това време.
След 24 февруари т.г. системата на международните отношения, завещана ни след Втората световна война, сякаш престана да съществува. Русия де факто не се ползва от привилегията да е част от клуба на т.нар. големи сили, представени от постоянните членки на Съвета за сигурност на ООН. Струва ли си да се поддадем на изкушението да мислим за свят след модела, заложен от държавите победителки, или по-скоро следва да запазим реда, докато не намерим с какво по-добро да заменим вече съществуващата система?
Много от държавите в Близкия изток сякаш гледат на войната в Украйна с оптимизъм. Западът игнорираше руските действия в Сирия и сега западните държави осъзнават, че това, което се случва в Украйна, е своеобразно повторение на сирийския сценарий. Ние непрекъснато повтаряхме, че Башар ал Асад следва правилата от Хама и Грозни и че Иран действа по един криминален начин в Сирия чрез своите милиции, извършващи масови убийства. Но Западът избра да сключи сделка с Русия, с Иран и с Ал Асад за сметка на сирийския народ и за сметка на задълбочаваща се криза в Близкия изток.
Мнозина в Близкия изток са някак скептични да последват действията на САЩ и ЕС спрямо Русия. Египет, Ирак и ключови държави от Залива са дори доста внимателни. Какво мислите за това?
Много малко е доверието в региона спрямо способността на САЩ или ЕС да отстояват своите позиции в Украйна. Видяхме, че и Вашингтон, и Брюксел сякаш признаха своето поражение в тази война, преди дори тя да е започнала. На президента Зеленски беше предложено той и семейството му да напуснат Украйна, докато САЩ и ЕС обсъждаха санкции, които да бъдат наложени едва след войната, а дори и по този въпрос нямаше съгласие. Да обсъждаш последиците от дадено събитие на практика означава да го приемеш за вече случило се. И страните в Залива и Ирак са непосредствено изложени на иранската заплаха и нямат никакво доверие, че САЩ ще ги защити. Египет се намира във фарватера на Залива, а режимът на Абделфатах ал Сиси не е в състояние да оцелее дори седмица без финансовата помощ на ОАЕ и Саудитска Арабия. Така виждам аз събитията.
Източник
 Dependencies
Dependencies